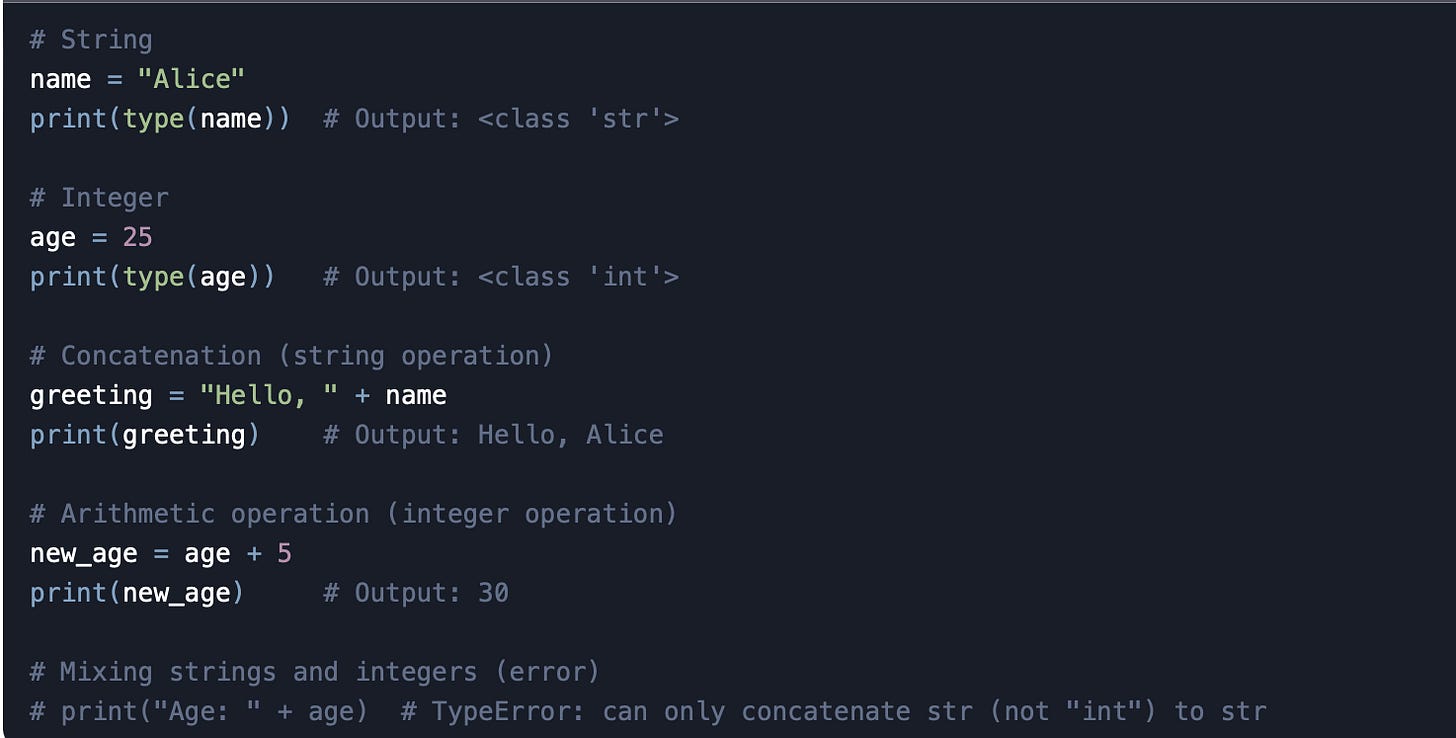
n Python, strings are sequences of characters enclosed in single (' '), double (" "), or triple quotes (''' ''' or """ """). They are used to represent text data. For example:
Key Characteristics of Strings:
Immutable: Once a string is created, it cannot be changed. Any operation that modifies a string creates a new string.
Sequence Type: Strings are sequences of characters, meaning you can access individual characters using indexing or slicing.
Text Representation: Strings are used to store and manipulate text data.
Differences Between Strings and Integers (or Other Variables):
Data Type:
Strings are of type
str.Integers are of type
int.Other variables can be of types like
float,list,dict, etc.
Usage:
Strings are used for text data.
Integers are used for whole numbers.
Other variables (like
float) are used for decimal numbers,listfor sequences of items, etc.
Operations:
Strings support operations like concatenation (
+), repetition (*), and slicing (my_string[0:5]).Integers support arithmetic operations like addition (
+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), etc.Mixing strings and integers directly in operations (e.g.,
"Hello" + 5) will raise aTypeError.
Representation:
Strings are enclosed in quotes.
Integers are written as plain numbers (e.g.,
42).
Examples:
To combine strings and integers, you need to convert the integer to a string using str():
In summary, strings are for text, integers are for whole numbers, and each type has its own set of operations and behaviors.